Smoking is a highly harmful habit, which causes 90% of all lung cancer deaths. More than 1.1 billion people in the world smoke tobacco, and it kills up to 50% of them (ASH).
The deadly consequences of tobacco use are due to the inhalation of more than 7,000 ingredients, like arsenic, carbon monoxide (it displaces oxygen on hemoglobin in red blood cell, so cells do not get the needed oxygen), butane (in lighter fluid), and tiny glass particles ( which cut up the lungs to improve nicotine delivery).
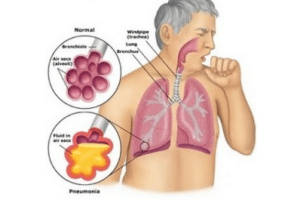
The inhalation of these chemicals causes lung-related issues, like lung cancer or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and the plaque deposits might also cause heart diseases, like heart attacks or congestive heart failure, as they damage the heart and blood vessel integrity.
Moreover, nicotine also increases cortisol (the stress hormone) and DHEA (the ‘all is good’ hormone) levels, but chronically elevated cortisol levels weaken the immune system.
This detrimental habit also contributes to:
- Insomnia
- Infertility
- Hormone imbalance
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Blood sugar issues
- Osteoporosis
Nicotine easily becomes addictive, and the withdrawal symptoms which appear quickly after you extinguish the cigarette are edginess and irritability, so you reach for a new one. It actually crosses the blood-brain barrier and leads to pleasant feelings by releasing dopamine.
This addiction is extremely powerful, and some even claim that it is more difficult to quit smoking than to give up the use of cocaine or heroin (ACS, 2015).
Continue Reading On Next Page (>) …